Why success rates matter
Fertility Associates has excellent IVF success rates, among the highest in Australasia. Success rates matter because the higher the success rate, the sooner we can get you pregnant. This gets you to your end point more quickly and will make your journey less costly.
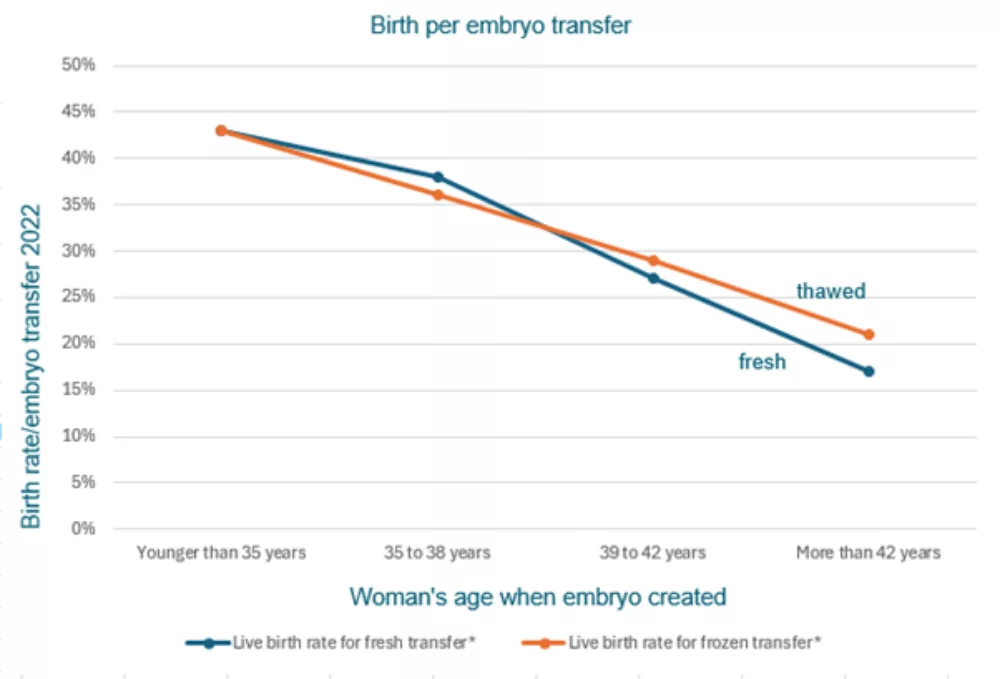
The Australian Reproductive Technology Accreditation Committee (RTAC) suggests clinics present results as birth rates per embryo transfer to allow easier comparison between clinics.
Birth rates are slightly higher when using fresh embryos - a fresh transfer always uses the best embryo, while thawed transfers use the next best embryo(s).
In nearly all our embryo transfers, only one embryo is transferred at a time to optimise the safety of both mother and child. ‘One at a time’ maximises your overall chance of a baby and your safety. These results exclude techniques that lift birth rates per transfer further, such as using donor eggs or Pre-implantation Genetic Screening (PGS).
Live birth rate for fresh transfer* |
Live birth rate for frozen transfer* |
|
Younger than 35 years |
43% |
43% |
35 to 38 years |
38% |
36% |
39 to 42 years |
27% |
29% |
More than 42 years |
17% |
21% |
* the average chance of a live birth, (take home baby rates), from embryo transfer of fresh and thawed embryos by age, for women using their own eggs, for treatment performed in 2022. Source: ANZARD data for 2022.
Your personalised chance of success
It is your personal chance of success per treatment that is important. The major factors contributing to individual success are:
- the woman’s age at egg collection
- the number of eggs collected
If you are using an egg donor, it is the donor’s age that matters. When using frozen embryos, it is your age when the embryos were created.
Your doctor will advise whether other personal factors, such as cause of infertility, weight, or sperm quality, that might affect your chance of success.
The numbers you are likely to have in an IVF cycle can be estimated from the level of a hormone called AMH (Anti Mullerian Hormone). Our doctors customise the dose of medications and the type of ovarian stimulation based on your age, AMH level, and other information from your medical history. Having 5-10 eggs gives about twice the chance compared to having 1-2 eggs. However, having more than 10 eggs only adds a small extra benefit.
The chance is very similar whether it is your first, second or third cycle, unless some major problem or issue shows up in the first cycle.
The number of eggs can vary from one IVF cycle to another: the number is usually within plus or minus 3 - so if you get 8 eggs the first time, you can expect 5 to 11 eggs the next time.
The power of persistence
No one who tries to become pregnant gives up if it doesn't happen in the first month of trying - the overall chance of success builds up each time you try. This is called the cumulative birth rate. The same applies to fertility treatments like IVF. If you do not become pregnant from your first IVF cycle, the chance of success in the second or third cycle is just as good.
The power of trying more than once is illustrated by our Fertility Cover® programme where an up-front fee covers up to three egg collection cycles of IVF and they receive a 70% refund if they do not have a baby.
When things don't go as expected...
IVF is a complex medical and scientific procedure so it's not surprising that unexpected things can sometimes happen. It's important to be aware of the downsides of treatment, when a treatment cycle doesn't go as expected.
In rare cases, there may be no eggs available for collection; those that are collected might not fertilize or develop into the blastocyst stage; not all eggs will survive the freezing and thawing process. Moreover, not all transferred embryos lead to pregnancy.
Rest assured, our team's success rates are among the best in Australasia and they are dedicated to providing the best care and support to optimize your chances for a successful outcome.
How we report our data
Different clinics report fertility treatment success in different ways. We use the chance of a baby from a single treatment cycle. This is also the preferred way to report results for the New Zealand consumer group, fertilityNZ and SART (the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology) in the United States
For IVF, this includes using both fresh and frozen embryos from a single egg collection. Over half our births from IVF in younger women come from using frozen embryos.
When selecting a clinic, it’s important to check what measure they use when reporting their success rates. Many use ‘clinical pregnancy per embryo transfer’, which excludes:
- People who do not have any eggs
- People whose eggs don’t fertilise
- Pregnancy loss or miscarriage
Clinical pregnancy rate per transfer can also be increased by transferring more than one embryo at a time, which carries the risks and complications of twins and even triplets to the mother and children.
Here are our most recent results for a single IVF egg collection cycle. It covers all women using their own eggs who have an egg collection, including those who did not get any eggs, those whose eggs didn’t fertilise, those who do not have an embryo suitable for transfer, and those whose pregnancy sadly miscarried.
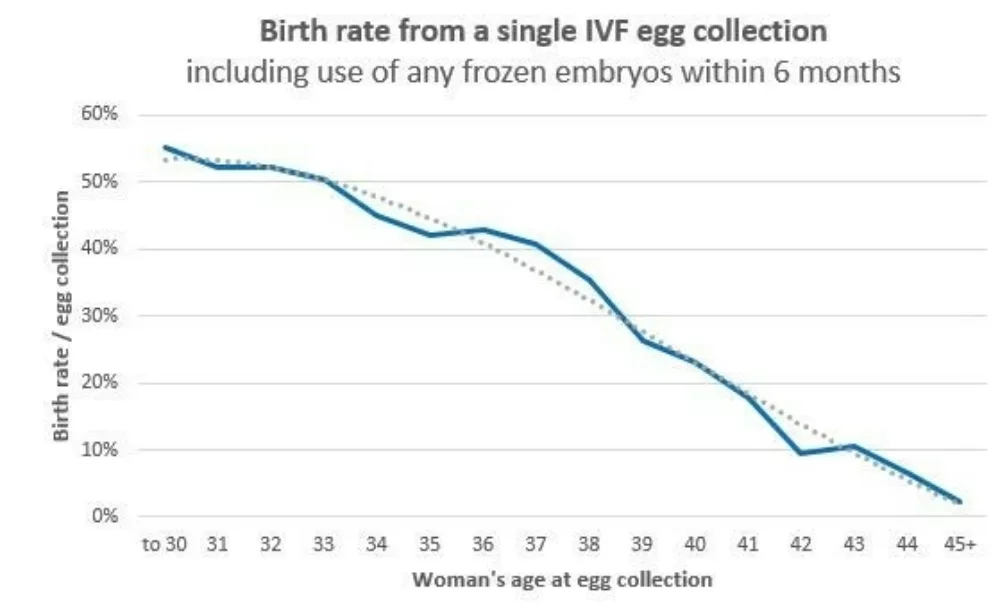
The figure above is based on all egg collections at Fertility Associates' clinics over the last three years for which we have complete birth results (2018-2020). These results cover IVF cycles with normal fertilisation and sperm microinjection.
We transfer fresh embryos at the cleavage or blastocyst stage, while thawed embryos are nearly always transferred at the blastocyst stage. About 10% of cycles started do not get to egg collection. For most of these people, it is better to stop, and start again with a higher dose of the medications used for ovarian stimulation.




